A popular AI detection tool has mistakenly flagged the Texas Declaration of Independence—drafted in 1836—as being written mainly by artificial intelligence.
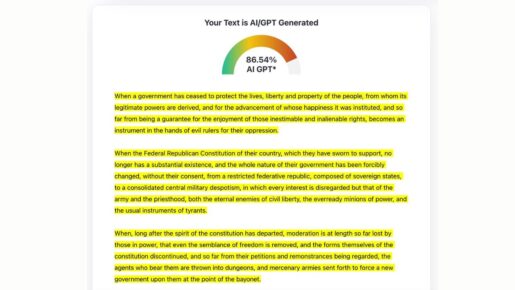
ZeroGPT, one of several widely used AI detectors, reported that the historic founding document of the Republic of Texas, the Texas Declaration of Independence, was 86.54% AI GPT. This means that it was flagged as being nearly 90% written with the assistance of artificial intelligence, even though the document was authored almost two centuries before the public release of AI language models.
The Dallas Express submitted two additional foundational documents from Texas history to test the platform’s consistency.
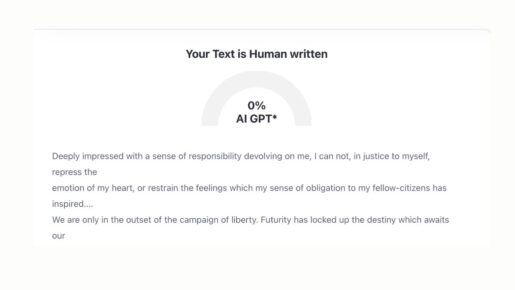
ZeroGPT rated “Sam Houston’s Inaugural Address as President of the Republic of Texas” (1836) a 0% AI GPT rating and declared it Human Written.
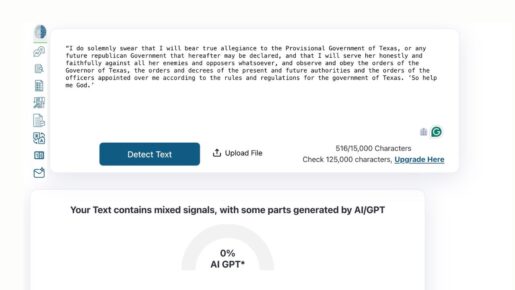
Yet the tool hedged when DX fed it the oath Davy Crockett and other volunteers took at Nacogdoches. Though the oath was rated at 0% AI GPT, the result warned the text contained mixed signals, suggesting AI GPT may have generated parts.
Of course, none of these documents can have been written by artificial intelligence. The Texas Declaration of Independence was signed by 59 delegates at Washington-on-the-Brazos in March 1836—nearly 190 years before the rise of ChatGPT and similar tools. Houston’s address was delivered aloud and reported widely by witnesses. Crockett’s oath was recorded in military rolls and firsthand accounts long before the invention of computers, let alone AI language models, which only became publicly accessible in 2023.
These flawed readings mirror earlier findings involving other historical texts.
In October 2024, Decrypt reported that ZeroGPT had labeled the U.S. Declaration of Independence as 97.93% AI-generated. That result prompted Christopher Penn, chief data scientist at Trust Insights, to publicly denounce AI detectors as a “joke.” warning they were “unsophisticated and harmful.”
“These tools are being used to do things like disqualify students, putting them on academic probation or suspension,” Penn told Decrypt. “That’s a very high-risk application.”
To Penn’s point, the Reddit thread R/utdallas shows an apparent UT Dallas student asking Redditors for advice after he claims two of his essays were flagged by his professor for being partially AI-written, something the student denies.
Despite their growing presence in academia and the workplace, AI detectors remain largely unregulated and prone to false positives.
In an experiment by Decrypt, four AI detectors—Grammarly, QuillBot, GPTZero, and ZeroGPT—were tested on a segment of the U.S. Declaration of Independence. Only Grammarly and QuillBot correctly identified it as fully human-written. ZeroGPT produced the worst result, although Grammarly recommended that Decrypt add citations.
The situation has drawn criticism from educators and technologists alike, particularly as detectors are increasingly used to discipline students suspected of cheating. While some companies, such as Grammarly and GPTZero, have added “authorship tools” to verify typing patterns and writing timelines, the tools remain opaque.
“It’s useful as a diagnostic tool,” GPTZero CTO Alex Cui told Decrypt, “but requires our authorship tools for a real solution.”
The core issue, according to Penn and others, is the overreliance on machine judgment for high-stakes decisions.
“If you’re going to kick someone out of college or revoke their doctoral degree, the false-positive rate has to be zero,” Penn said. “There’s not a single tool on the market that can meet that bar.”